EFAP Procedures Manual Section 2: Introduction to EFAP
All WSDA FA EFAP forms and publications listed in this section are found here.
2.1 Definitions
Acquisition Cost: The total costs incurred in acquiring and readying an asset for its intended use, including the cost of modifications, accessories, and ancillary charges.
Administration Cap: EFAP Lead Agencies are limited to twenty percent (20%) administrative costs of the total award regardless of the number of functions they perform (e.g., Lead Agency, Food Pantry, Food Bank). An EFAP Sub Agency (Food Bank/Food Pantry) is limited to fifteen percent (15%) of their individual award total for administrative costs. The Administration Cap includes administrative direct expenses and indirect expenses but excludes the "up to one percent (1%)" of the total award for allowable dues.
Administrative Expenses: The expenses incurred in the overall operation and management of the organization that are direct billed. Salaries, wages, supplies, general expenses, and membership dues that are direct billed.
Agreement: A written agreement (Grant – state funding, Subaward – federal funding) between the Washington State Department of Agriculture (WSDA) Food Assistance (FA) and the Lead Agency identifying the rights and obligations of both parties governed by the Agreement, including the following of exhibits, attachments or other documents incorporated by reference.
Ancillary Charges: The expenses involved in the transaction, but not directly related or incidental. This includes items such as taxes, duty, transit insurance, freight, and installation may be included in the acquisition cost, in accordance with the participating organization’s accounting practices.
Assistance Listing Number: Assistance listings are detailed public descriptions of federal programs that provide grants, loans, scholarships, insurance, and other types of assistance awards.
Authorized Representative: For FA, means the FA designee authorized in writing to act on the Director’s behalf; for the Lead Agency means the Authorized Signer.
Authorized Signature: Signature of the board president, tribal chairperson, agency director, or other official authorized to sign.
Biennial Meetings: Prior to the start of each biennium, the current Lead Agency for each county is required to hold a local meeting (or multiple meetings) to lay the groundwork for the next two-year EFAP Agreement period. The purpose of the meeting is to give EFAP Food Pantries an opportunity to vote and voice their opinion on how the funds would best serve their county, or multi-county region. Additionally, these meetings determine which organizations will be participating (Lead Agency, Food Banks, Food Pantries) in the upcoming biennium.
Capital Assets: Tangible or intangible assets used in operations having a useful life of more than one (1) year which are capitalized in accordance with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). See Federal Guidance 2 CFR §§ 200.1 and 200.465.
Capital Improvement Project: The actual additions, improvements, modifications, replacements, rearrangements, reinstallations, renovations, or alterations to property, infrastructure, or facilities that increase their value or useful life (not ordinary repairs and maintenance), has a per unit cost which equals or exceeds the lesser of the capitalization level established by the organization for financial statement purposes, of $10,000 (if procured October 1, 2024, or thereafter).
Capitalization Policy: The criteria used by an organization to determine which capital expenditure should be reported as a capital asset. Capital assets with a unit cost (including ancillary costs) of $10,000 or greater, or collections of capital assets with a total cost of $10,000 or greater, are capitalized, unless otherwise noted.
Contract: A written Agreement between FA and the Contractor/Vendor identifying the rights and obligations of both parties governed by the Contract, including the following of exhibits, attachments or other documents incorporated by reference.
Coordinated Services: Making contact with and sharing information about other programs and establishing procedures for referring clients between food pantries and other services.
Current Fair Market Value: The value of equipment and supplies determined by selling them in a competitive market or by researching advertised prices for similar items on the used market.
Davis-Bacon Act: Federal law requiring the payment of prevailing wage in certain contracts (minimum threshold of $2,000.00) for the construction, alteration, or repair (including painting and decorating) of public buildings or public works supported with federal funding and required by the fund source. Exceptions may apply.
Debarment, Suspension, and Ineligibility: The act of being suspended or being declared ineligible by any state or federal agency from participating in any transactions with them. Also referred to as suspension and debarment. Lead Agency certification is required in all written Agreements that indicates neither they nor their principals are not presently debarred, declared ineligible, or voluntarily excluded from participation in transactions by the state of Washington and, if federal funds are a source of funding, any federal department or agency.
Direct Client Services: Conducting programming that has direct contact with clients such as food distribution and/or certifying clients for a program or services.
Duplication of Service: This may be determined when two food pantries provide the same services, on the same days, around the same time, in a similar geographical area, focusing on a similar population with similar food offerings. This seldom occurs.
EFAP Client: A person who is in need of food and resides in the state of Washington. Client counts include the total number of individuals in a household receiving food from an EFAP Food Pantry. Documentation is never required for EFAP.
EFAP Household: The client or clients who share food at a residence or home make up one household. Household counts include the total number of households that receive food from an EFAP Food Pantry. Documentation is never required for EFAP.
Emergency Food: Food that is given to clients who do not have the means to acquire that food themselves, so that they will not go hungry.
Emergency Food Assistance Program (EFAP): A program administered by FA which provides funding to help support Food Pantries.
Emergency Food Assistance Program (EFAP)-Tribal: A program administered by FA which provides funding to help support EFAP-Tribal Food Pantry and Voucher Programs.
Equipment: Tangible personal property (including information technology systems) that has a useful life of more than one year, is movable, and has a per-unit acquisition cost which equals or exceeds the lesser of the capitalization level established by the non-federal entity (organization) for financial statement purposes, or $10,000.
Equipment Repairs: Equipment repairs with a cost of $10,000 or more are considered a capital expenditure and should be capitalized when they prolong the useful life of the equipment being repaired. Equipment repair costs when they prolong the useful life of the equipment being repaired. Equipment repair costs which equal or exceed the lesser of the capitalization level established by the non-federal entity (organization) for financial statement purposes, or $10,000.
Food Assistance (FA): Washington State Department of Agriculture (WSDA) Food Assistance (FA) and its programs.
Food Assistance Advisory Committee (FAAC): Part of the Washington Food Coalition (WFC) that makes recommendations to FA for program and policy improvements.
Food Bank: An organization that collects, warehouses, and distributes food, including perishable foods, or other products to hunger relief organizations and is selected by EFAP Food Pantries to serve in that role. Also referred to as a provider.
Food Pantry: An eligible hunger relief organization that distributes predominately unprepared food without charge to its clients and is selected to participate in EFAP. The organization must provide direct client services, food storage, and distribution with consistency. Also referred to as a provider.
Food Pantry Client: Clients who receive a food distribution at a participating EFAP Food Pantry.
Indirect Expenses: The general overhead expenses of an organization that cannot be readily identified with a particular program.
Interested Party: Any agency, tribe, or tribal organization wishing to be considered as an EFAP Lead Agency, Food Bank, or Food Pantry.
Lead Agency: The entity that holds a written Agreement with Washington State Department of Agriculture (WSDA) to implement the program at the local level and/or through its Sub Agencies. The term Grantee is used for state pass-through funded grants. The term Subrecipient is used for federal pass-through funded subawards. Also referred to as a provider.
Match Requirements: The provider’s required contribution of cash and/or in-kind contributions to participate in EFAP.
Meal Program: An emergency food assistance provider that provides predominately low-income clients prepared meals in a congregate setting. Meal Programs are ineligible for participation in EFAP and may not be supported with EFAP food or funding.
Mobile Food Pantry: An eligible hunger relief organization that distributes unprepared food without charge to its clients and is selected to participate in EFAP. The organization must provide direct client services, food storage, and distribution with consistency. A food distributor that travels to communities, oftentimes with a regular or semi-regular distribution schedule.
Modified Total Direct Cost (MTDC): All direct salaries and wages, applicable fringe benefits, materials and supplies, services, travel, and up to the first $50,000 of each subaward (regardless of the period of performance of the subawards under the award). MTDC excludes equipment, capital expenditures, rental costs, and the portion of each subaward in excess of $50,000.
New Client: The first time a client visits ANY EFAP Food Pantry in the state of Washington in a calendar year (starting January 1 of each year).
Nonprofit: A private agency or organization with 501(c)(3) tax-exempt status under the Internal Revenue Code, or that has applied for 501(c)(3) tax-exempt status with the Internal Revenue Service.
Nonprofit Corporation: A nonprofit entity recognized by and currently registered with the state of Washington Corporations Division of the Secretary of State or is specifically exempt from the requirement to register.
Operational Expenses: Costs that are clearly identifiable with providing direct services to clients or distribution services to EFAP Food Pantries.
Ordinary Maintenance and Repair Costs: Costs incurred for utilities, insurance, security, necessary maintenance, janitorial services, repair, or upkeep of buildings and equipment (including federal property unless otherwise provided for) which neither add to the permanent value of the property nor appreciably prolong its intended life, but keep it in an efficient operating condition, are allowable. These costs are only allowable to the extent not paid through rental or other agreements.
Period of Performance: The timeframe when an eligible program expense may be incurred and includes additional time for fiscal closeout of each fiscal year as defined in the written Agreement.
Period of Use: The additional length of time beyond the period of performance for which equipment and capital improvements must be in use, per program requirements and procurement guidelines.
Personally Identifiable Information (PII): Information identifiable to any person, including, but not limited to, information that relates to a person’s name, health, finances, education, business, use or receipt of governmental services or other activities, addresses, telephone numbers, social security numbers, driver license numbers, other identifying numbers, and any financial identifiers, and “Protected Health Information” under the federal Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA) Public Law No. 104-191, § 264, 110 Stat. 1936, any financial identifiers, and other information that may be exempt from public disclosure or other unauthorized persons under state and federal statutes.
Program Review: Any planned, ongoing, or periodic activity that measures and ensures Lead Agency and Sub Agency compliance with the terms, conditions, and requirements of an Agreement. Monitoring for program reviews will be based on a risk assessment of the ability to deliver services and its performance in delivering those services under the terms of the Agreement. It could be on-site, virtual (desk review), or hybrid (on-site/virtual). Also referred to as a compliance review.
Provider: Any organization or tribe that is participating in any FA program by written Agreement.
RCW: Revised Code of Washington.
Returning Client: Any subsequent visit a client makes to ANY EFAP Food Pantry in the state of Washington in a calendar year (starting January 1 of each year).
Sealed Bid: Bids are publicly solicited, and a firm fixed price contract (lump sum or unit price) is awarded to the responsible bidder whose bid, conforming with all the material terms and conditions of the invitation for the bids, is the lowest in price.
Single Audit: An organization-wide audit of an entity that expends $1,000,000 (for fiscal years beginning October 1, 2024 or later) or more of federal assistance (funds, grants, awards) as required by 2 CFR Part 200, Uniform Administrative Requirements, Cost Principals, and Audit Requirements for Federal Awards.
Sponsored Site: Any site or program used for distribution of food that the participating agency doesn't directly operate, manage, or maintain including any on-site Food Pantry, any off-site temporary distribution location, mobile Food Pantry, or homebound delivery program, or meal program.
State: The state of Washington.
State Prevailing Wage: The state law requiring the payment of prevailing wage in certain contracts for the construction, alteration, or repair (including painting and decorating) of public buildings or public works.
Sub Agency: The entity that holds a written Agreement with a Lead Agency to implement the program at the local level. The term Subgrantee is used for state pass-through funded grants. The Agreement between the Lead Agency and Sub Agency for state pass-through is also referred to as a subgrant.
Uniform Guidance: 2 CFR Part 200, Uniform Administrative Requirements, Cost Principles, and Audit Requirements for Federal Awards.
Vendor: An entity that provides goods or services on a fee-for-service or per-unit basis with contractual penalties if the entity fails to meet program performance standards. Also known as a Contractor. The designation of Contractor/Vendor will be identified in any written Agreement.
WAC: Washington Administrative Code.
Washington Food Coalition (WFC): A nonprofit organization that advocates for the emergency food system and provides education and training to a statewide membership of Food Banks, Food Pantries, meal programs, state agencies and other partners. WFC also houses the Food Assistance Advisory Committee, which acts as an advisory body to FA.
WSDA: The Washington State Department of Agriculture or its successor agency, if any.
Administration Cap: EFAP Lead Agencies are limited to twenty percent (20%) administrative costs of the total award regardless of the number of functions they perform (e.g., Lead Agency, Food Pantry, Food Bank). An EFAP Sub Agency (Food Bank/Food Pantry) is limited to fifteen percent (15%) of their individual award total for administrative costs. The Administration Cap includes administrative direct expenses and indirect expenses but excludes the "up to one percent (1%)" of the total award for allowable dues.
Administrative Expenses: The expenses incurred in the overall operation and management of the organization that are direct billed. Salaries, wages, supplies, general expenses, and membership dues that are direct billed.
Agreement: A written agreement (Grant – state funding, Subaward – federal funding) between the Washington State Department of Agriculture (WSDA) Food Assistance (FA) and the Lead Agency identifying the rights and obligations of both parties governed by the Agreement, including the following of exhibits, attachments or other documents incorporated by reference.
Ancillary Charges: The expenses involved in the transaction, but not directly related or incidental. This includes items such as taxes, duty, transit insurance, freight, and installation may be included in the acquisition cost, in accordance with the participating organization’s accounting practices.
Assistance Listing Number: Assistance listings are detailed public descriptions of federal programs that provide grants, loans, scholarships, insurance, and other types of assistance awards.
Authorized Representative: For FA, means the FA designee authorized in writing to act on the Director’s behalf; for the Lead Agency means the Authorized Signer.
Authorized Signature: Signature of the board president, tribal chairperson, agency director, or other official authorized to sign.
Biennial Meetings: Prior to the start of each biennium, the current Lead Agency for each county is required to hold a local meeting (or multiple meetings) to lay the groundwork for the next two-year EFAP Agreement period. The purpose of the meeting is to give EFAP Food Pantries an opportunity to vote and voice their opinion on how the funds would best serve their county, or multi-county region. Additionally, these meetings determine which organizations will be participating (Lead Agency, Food Banks, Food Pantries) in the upcoming biennium.
Capital Assets: Tangible or intangible assets used in operations having a useful life of more than one (1) year which are capitalized in accordance with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). See Federal Guidance 2 CFR §§ 200.1 and 200.465.
- Capital assets include land, buildings (facilities), equipment, equipment repair, and intellectual property (including software) whether acquired by purchase, construction, manufacture, lease-purchase, exchange, or through capital lease. FA funding is not to be utilized for the purchase of land or new buildings. Some exceptions may apply.
- Capital assets do not include intangible right-to-use assets and right-to-use operating lease assets. For example, capitalized assets that recognize a lessee's right to control the use of property and/or equipment for a period of time under a lease contract.
Capital Improvement Project: The actual additions, improvements, modifications, replacements, rearrangements, reinstallations, renovations, or alterations to property, infrastructure, or facilities that increase their value or useful life (not ordinary repairs and maintenance), has a per unit cost which equals or exceeds the lesser of the capitalization level established by the organization for financial statement purposes, of $10,000 (if procured October 1, 2024, or thereafter).
Capitalization Policy: The criteria used by an organization to determine which capital expenditure should be reported as a capital asset. Capital assets with a unit cost (including ancillary costs) of $10,000 or greater, or collections of capital assets with a total cost of $10,000 or greater, are capitalized, unless otherwise noted.
Contract: A written Agreement between FA and the Contractor/Vendor identifying the rights and obligations of both parties governed by the Contract, including the following of exhibits, attachments or other documents incorporated by reference.
Coordinated Services: Making contact with and sharing information about other programs and establishing procedures for referring clients between food pantries and other services.
Current Fair Market Value: The value of equipment and supplies determined by selling them in a competitive market or by researching advertised prices for similar items on the used market.
Davis-Bacon Act: Federal law requiring the payment of prevailing wage in certain contracts (minimum threshold of $2,000.00) for the construction, alteration, or repair (including painting and decorating) of public buildings or public works supported with federal funding and required by the fund source. Exceptions may apply.
Debarment, Suspension, and Ineligibility: The act of being suspended or being declared ineligible by any state or federal agency from participating in any transactions with them. Also referred to as suspension and debarment. Lead Agency certification is required in all written Agreements that indicates neither they nor their principals are not presently debarred, declared ineligible, or voluntarily excluded from participation in transactions by the state of Washington and, if federal funds are a source of funding, any federal department or agency.
Direct Client Services: Conducting programming that has direct contact with clients such as food distribution and/or certifying clients for a program or services.
Duplication of Service: This may be determined when two food pantries provide the same services, on the same days, around the same time, in a similar geographical area, focusing on a similar population with similar food offerings. This seldom occurs.
EFAP Client: A person who is in need of food and resides in the state of Washington. Client counts include the total number of individuals in a household receiving food from an EFAP Food Pantry. Documentation is never required for EFAP.
EFAP Household: The client or clients who share food at a residence or home make up one household. Household counts include the total number of households that receive food from an EFAP Food Pantry. Documentation is never required for EFAP.
Emergency Food: Food that is given to clients who do not have the means to acquire that food themselves, so that they will not go hungry.
Emergency Food Assistance Program (EFAP): A program administered by FA which provides funding to help support Food Pantries.
Emergency Food Assistance Program (EFAP)-Tribal: A program administered by FA which provides funding to help support EFAP-Tribal Food Pantry and Voucher Programs.
Equipment: Tangible personal property (including information technology systems) that has a useful life of more than one year, is movable, and has a per-unit acquisition cost which equals or exceeds the lesser of the capitalization level established by the non-federal entity (organization) for financial statement purposes, or $10,000.
Equipment Repairs: Equipment repairs with a cost of $10,000 or more are considered a capital expenditure and should be capitalized when they prolong the useful life of the equipment being repaired. Equipment repair costs when they prolong the useful life of the equipment being repaired. Equipment repair costs which equal or exceed the lesser of the capitalization level established by the non-federal entity (organization) for financial statement purposes, or $10,000.
Food Assistance (FA): Washington State Department of Agriculture (WSDA) Food Assistance (FA) and its programs.
Food Assistance Advisory Committee (FAAC): Part of the Washington Food Coalition (WFC) that makes recommendations to FA for program and policy improvements.
Food Bank: An organization that collects, warehouses, and distributes food, including perishable foods, or other products to hunger relief organizations and is selected by EFAP Food Pantries to serve in that role. Also referred to as a provider.
Food Pantry: An eligible hunger relief organization that distributes predominately unprepared food without charge to its clients and is selected to participate in EFAP. The organization must provide direct client services, food storage, and distribution with consistency. Also referred to as a provider.
Food Pantry Client: Clients who receive a food distribution at a participating EFAP Food Pantry.
Indirect Expenses: The general overhead expenses of an organization that cannot be readily identified with a particular program.
- For the purposes of EFAP, the participating agency may elect to use their federal negotiated indirect cost rate or the federal de minimis indirect cost rate of fifteen percent (15%). May not exceed the Administration Cap.
Interested Party: Any agency, tribe, or tribal organization wishing to be considered as an EFAP Lead Agency, Food Bank, or Food Pantry.
Lead Agency: The entity that holds a written Agreement with Washington State Department of Agriculture (WSDA) to implement the program at the local level and/or through its Sub Agencies. The term Grantee is used for state pass-through funded grants. The term Subrecipient is used for federal pass-through funded subawards. Also referred to as a provider.
Match Requirements: The provider’s required contribution of cash and/or in-kind contributions to participate in EFAP.
Meal Program: An emergency food assistance provider that provides predominately low-income clients prepared meals in a congregate setting. Meal Programs are ineligible for participation in EFAP and may not be supported with EFAP food or funding.
Mobile Food Pantry: An eligible hunger relief organization that distributes unprepared food without charge to its clients and is selected to participate in EFAP. The organization must provide direct client services, food storage, and distribution with consistency. A food distributor that travels to communities, oftentimes with a regular or semi-regular distribution schedule.
Modified Total Direct Cost (MTDC): All direct salaries and wages, applicable fringe benefits, materials and supplies, services, travel, and up to the first $50,000 of each subaward (regardless of the period of performance of the subawards under the award). MTDC excludes equipment, capital expenditures, rental costs, and the portion of each subaward in excess of $50,000.
New Client: The first time a client visits ANY EFAP Food Pantry in the state of Washington in a calendar year (starting January 1 of each year).
Nonprofit: A private agency or organization with 501(c)(3) tax-exempt status under the Internal Revenue Code, or that has applied for 501(c)(3) tax-exempt status with the Internal Revenue Service.
Nonprofit Corporation: A nonprofit entity recognized by and currently registered with the state of Washington Corporations Division of the Secretary of State or is specifically exempt from the requirement to register.
Operational Expenses: Costs that are clearly identifiable with providing direct services to clients or distribution services to EFAP Food Pantries.
Ordinary Maintenance and Repair Costs: Costs incurred for utilities, insurance, security, necessary maintenance, janitorial services, repair, or upkeep of buildings and equipment (including federal property unless otherwise provided for) which neither add to the permanent value of the property nor appreciably prolong its intended life, but keep it in an efficient operating condition, are allowable. These costs are only allowable to the extent not paid through rental or other agreements.
Period of Performance: The timeframe when an eligible program expense may be incurred and includes additional time for fiscal closeout of each fiscal year as defined in the written Agreement.
Period of Use: The additional length of time beyond the period of performance for which equipment and capital improvements must be in use, per program requirements and procurement guidelines.
Personally Identifiable Information (PII): Information identifiable to any person, including, but not limited to, information that relates to a person’s name, health, finances, education, business, use or receipt of governmental services or other activities, addresses, telephone numbers, social security numbers, driver license numbers, other identifying numbers, and any financial identifiers, and “Protected Health Information” under the federal Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA) Public Law No. 104-191, § 264, 110 Stat. 1936, any financial identifiers, and other information that may be exempt from public disclosure or other unauthorized persons under state and federal statutes.
Program Review: Any planned, ongoing, or periodic activity that measures and ensures Lead Agency and Sub Agency compliance with the terms, conditions, and requirements of an Agreement. Monitoring for program reviews will be based on a risk assessment of the ability to deliver services and its performance in delivering those services under the terms of the Agreement. It could be on-site, virtual (desk review), or hybrid (on-site/virtual). Also referred to as a compliance review.
Provider: Any organization or tribe that is participating in any FA program by written Agreement.
RCW: Revised Code of Washington.
Returning Client: Any subsequent visit a client makes to ANY EFAP Food Pantry in the state of Washington in a calendar year (starting January 1 of each year).
Sealed Bid: Bids are publicly solicited, and a firm fixed price contract (lump sum or unit price) is awarded to the responsible bidder whose bid, conforming with all the material terms and conditions of the invitation for the bids, is the lowest in price.
Single Audit: An organization-wide audit of an entity that expends $1,000,000 (for fiscal years beginning October 1, 2024 or later) or more of federal assistance (funds, grants, awards) as required by 2 CFR Part 200, Uniform Administrative Requirements, Cost Principals, and Audit Requirements for Federal Awards.
Sponsored Site: Any site or program used for distribution of food that the participating agency doesn't directly operate, manage, or maintain including any on-site Food Pantry, any off-site temporary distribution location, mobile Food Pantry, or homebound delivery program, or meal program.
State: The state of Washington.
State Prevailing Wage: The state law requiring the payment of prevailing wage in certain contracts for the construction, alteration, or repair (including painting and decorating) of public buildings or public works.
Sub Agency: The entity that holds a written Agreement with a Lead Agency to implement the program at the local level. The term Subgrantee is used for state pass-through funded grants. The Agreement between the Lead Agency and Sub Agency for state pass-through is also referred to as a subgrant.
Uniform Guidance: 2 CFR Part 200, Uniform Administrative Requirements, Cost Principles, and Audit Requirements for Federal Awards.
Vendor: An entity that provides goods or services on a fee-for-service or per-unit basis with contractual penalties if the entity fails to meet program performance standards. Also known as a Contractor. The designation of Contractor/Vendor will be identified in any written Agreement.
WAC: Washington Administrative Code.
Washington Food Coalition (WFC): A nonprofit organization that advocates for the emergency food system and provides education and training to a statewide membership of Food Banks, Food Pantries, meal programs, state agencies and other partners. WFC also houses the Food Assistance Advisory Committee, which acts as an advisory body to FA.
WSDA: The Washington State Department of Agriculture or its successor agency, if any.
2.2 Program History
Emergency Food Assistance Program (EFAP) and EFAP-Tribal
EFAP and EFAP-Tribal are state-run programs that were established in 1986 to support food-insecure households in Washington State (currently estimated as high as one in five people), including people experiencing homelessness. Through this state funded program, financial support is provided to participating agencies (Lead Agencies, Tribes, Tribal Organizations, Food Banks, and Food Pantries) to help offset the costs of providing hunger relief services (such as food, equipment, training, repairs, and operational expenses). The EFAP-Tribal Food Pantry and Voucher program history are outlined in the EFAP-Tribal Procedures Manual.
EFAP is ever evolving to meet the current needs of food-insecure Washingtonians; over the past few years, statewide programmatic improvements have included reducing client access barriers (no documentation required for service), increased access (removal of geographical restrictions for service) and increased nutritious and culturally relevant food offerings. Future updates aim to increase program participation and overall understanding by providing guidance and training to hunger relief organizations seeking involvement in EFAP for the first time.
EFAP is a program designed to empower organizations on the local level to make decisions that address the diverse needs of each area of the state, county by county. Every two years at Biennial Meetings, participating organizations (Lead Agencies and Sub Agencies) vote through a democratic process to determine how county allocations* will be utilized in service to that community and select participating organizations.
Funding for EFAP has never covered all costs of hunger relief, but it is foundational for a critical program that addresses the essential needs of food-insecure Washingtonians. Food insecurity has grown since COVID-19 and hunger relief organizations have fought tenaciously to meet the rising demand. Additionally, organizations have faced unanticipated costs such as supply chain disruptions, and rising operational and food costs. The state legislature and federal government continue to provide additional funding and support during this time for these and other unforeseen challenges and to help fill critical gaps.
There is more work to do, and we are excited to partner with you – to continue improving EFAP and to help feed our neighbors. For more on future EFAP improvements, see Recommendations for the Emergency Food Assistance Program (josh martinez, CEO, Future Emergent).
*Funds are strategically allocated to each county based on poverty data (American Community Survey 5-year data at 200% Federal Poverty Level) with a county base of $20,000 that supports remote and rural areas.
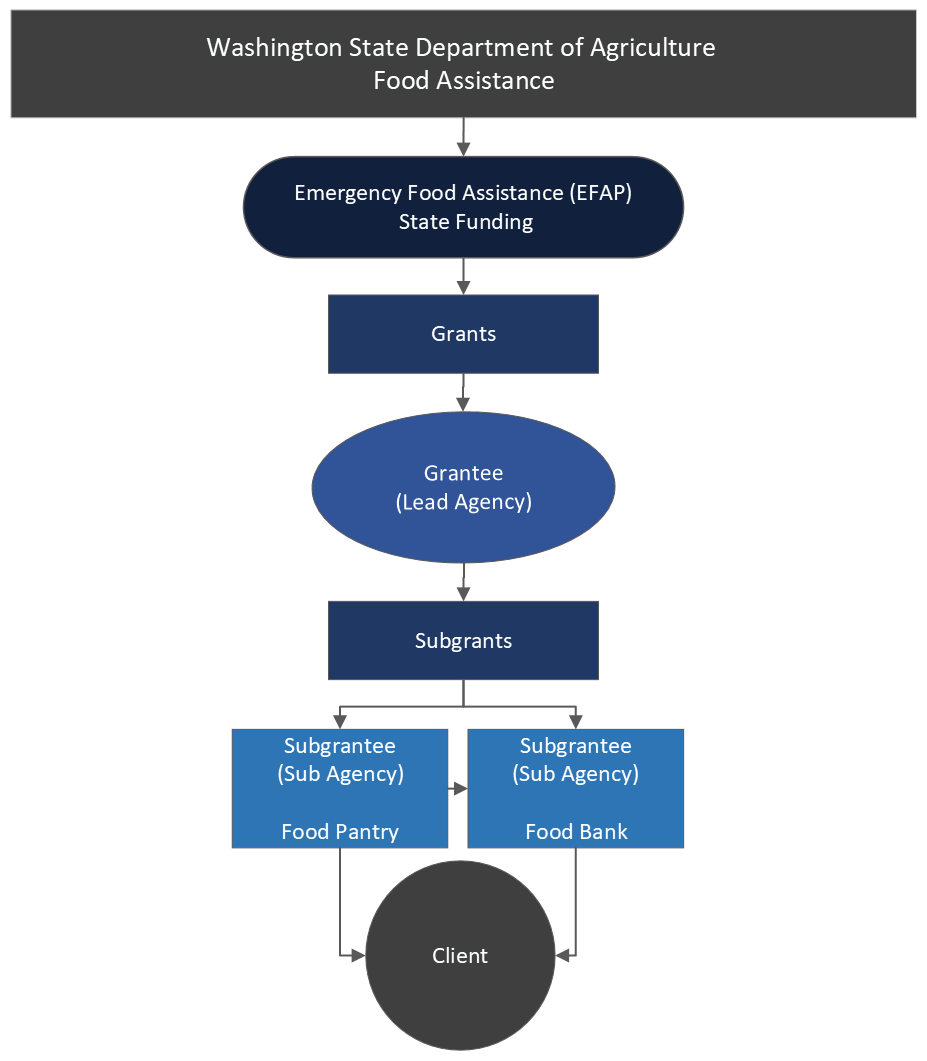
EFAP and EFAP-Tribal are state-run programs that were established in 1986 to support food-insecure households in Washington State (currently estimated as high as one in five people), including people experiencing homelessness. Through this state funded program, financial support is provided to participating agencies (Lead Agencies, Tribes, Tribal Organizations, Food Banks, and Food Pantries) to help offset the costs of providing hunger relief services (such as food, equipment, training, repairs, and operational expenses). The EFAP-Tribal Food Pantry and Voucher program history are outlined in the EFAP-Tribal Procedures Manual.
EFAP is ever evolving to meet the current needs of food-insecure Washingtonians; over the past few years, statewide programmatic improvements have included reducing client access barriers (no documentation required for service), increased access (removal of geographical restrictions for service) and increased nutritious and culturally relevant food offerings. Future updates aim to increase program participation and overall understanding by providing guidance and training to hunger relief organizations seeking involvement in EFAP for the first time.
EFAP is a program designed to empower organizations on the local level to make decisions that address the diverse needs of each area of the state, county by county. Every two years at Biennial Meetings, participating organizations (Lead Agencies and Sub Agencies) vote through a democratic process to determine how county allocations* will be utilized in service to that community and select participating organizations.
Funding for EFAP has never covered all costs of hunger relief, but it is foundational for a critical program that addresses the essential needs of food-insecure Washingtonians. Food insecurity has grown since COVID-19 and hunger relief organizations have fought tenaciously to meet the rising demand. Additionally, organizations have faced unanticipated costs such as supply chain disruptions, and rising operational and food costs. The state legislature and federal government continue to provide additional funding and support during this time for these and other unforeseen challenges and to help fill critical gaps.
There is more work to do, and we are excited to partner with you – to continue improving EFAP and to help feed our neighbors. For more on future EFAP improvements, see Recommendations for the Emergency Food Assistance Program (josh martinez, CEO, Future Emergent).
*Funds are strategically allocated to each county based on poverty data (American Community Survey 5-year data at 200% Federal Poverty Level) with a county base of $20,000 that supports remote and rural areas.

2.3 EFAP Process and Allocations
- EFAP Agreements cover a two-year period.
- EFAP Agreements will begin the first day of the biennium, July 1, and end two years later, the last day of the biennium, June 30.
- For the biennium, EFAP will be supported with state funds. Food Assistance (FA) will issue a Lead Agency EFAP Grant Agreement. The Lead Agency will in turn enter into EFAP Sub Agency Agreements with their Sub Agencies.
- Key steps in the process:
- Current Lead Agencies prepare for the Biennial Meetings.
- Current Lead Agencies conduct Biennial Meetings.
- Elected Lead Agencies complete Applications and send to FA.
- FA finalizes Agreements with Lead Agencies.
- Lead Agencies finalize Agreements with Sub Agencies.
- On-going Compliance Management & Communications.
- FA computes the allocation of funds to counties.
- FA computes county allocations based on a formula determined in consultation with the Food Assistance Advisory Committee (FAAC) and the EFAP Survey circulated to Lead Agencies.
- Every county receives a base amount of $20,000 each fiscal year.
- The remaining funds shall be distributed by each county's percentage of the state’s population with incomes at or below 200% of the Federal Poverty Guidelines based on the current 5-year average Census Bureau’s American Community Survey data.
- Any other funds will be allocated at the time and for the purpose authorized by the Washington State Legislature.
- FA computes county allocations based on a formula determined in consultation with the Food Assistance Advisory Committee (FAAC) and the EFAP Survey circulated to Lead Agencies.
2.4 Interested Parties
EFAP is a program designed to empower organizations on the local level to make decisions that address the diverse needs of each area of the state, county by county. Every two years at Biennial Meetings, participating organizations (Lead Agencies and Sub Agencies) vote through a democratic process to determine how county allocations will be utilized in service to that community and select any new eligible participating organizations to serve in the following capacity: Lead Agency, Food Bank Sub Agency, and Food Pantry Sub Agency.
Please contact Food Assistance (FA) for further guidance if you are a tribe or tribal organization that is not currently participating in the EFAP-Tribal Food Pantry or Voucher Program.
Please contact Food Assistance (FA) for further guidance if you are a tribe or tribal organization that is not currently participating in the EFAP-Tribal Food Pantry or Voucher Program.
- Interested in becoming a Lead Agency?
- Any organization interested in becoming an EFAP Lead Agency may submit a letter of interest to FA immediately or no less than two weeks before the scheduled biennial meeting. The letter of interest must address the specific requirements of Section 5.1, Lead Agency Eligibility Criteria of this manual. FA will evaluate the letter of interest based on the interest based on the criteria listed in the FA Interested Party Lead Agency Eligibility Verification Checklist (AGR-8007).
- FA will respond to the letter of interest within 60 days of receipt. The response will be to inform the requesting agency of their eligibility status only and is not a guarantee of participation in the program as a Lead Agency. FA will notify the county Lead Agency if the interested party is eligible for the Lead Agency role.
- Note: Interested parties must submit a letter of interest in advance of each biennium. Letters of interest from a previous biennium will not be considered.
- Prospective organizations and existing Lead Agencies interested in operating EFAP must send a letter of interest to FA (foodassistance@agr.wa.gov) that:
- Addresses the criteria listed in the Lead Agency Letter of Interest Eligibility Verification Checklist.
- The prospective Lead Agency must make apparent on the checklist that it:
- Meets minimum requirements, provide certification, have management capabilities, and contracting abilities.
- Indicates their interest in being considered for county Lead Agency. The letter of interest must include:
- Interested Party Contact information:
- Agency information.
- Name, business address, primary operating county.
- Contact information:
- Name, title, phone number, email address;
- County(ies) in which your organization seeks to provide EFAP Lead Agency services. Business description, qualifications, experience managing agreements, and the organization’s specific work related to hunger-relief:
- A description of how the interested organization would deliver EFAP services and operate the program in accordance with state and federal regulations.
- Identify any challenges or benefits this might have on the county’s current emergency food assistance system.
- Interested Party Contact information:
- Eligibility; assurance that interested party meets the eligibility criteria:
- IRS 501(c)(3), public agency, or federally recognized tribe.
- Active WA SOS Corporation registration.
- Active SAM.GOV registration.
- Board (or equivalent) support for this new role. This may be a vote to support the action, a letter of support, etc.
- The prospective Lead Agency must make apparent on the checklist that it:
- Addresses the criteria listed in the Lead Agency Letter of Interest Eligibility Verification Checklist.
- Note: Biennial Meetings are hosted prior to the start of the new biennium, starting in April and running through early June before the deadline to submit applications.
- FA requires a minimum of 2 weeks (preferably 30 days) prior to the scheduled Biennial Meeting to evaluate the eligibility of a prospective Lead Agency.
- FA will:
- Conduct a site visit (in-person or virtual).
- Notify the Interested Party and current Lead Agency of the former's eligibility status in writing prior to the scheduled Biennial Meeting.
- Connect eligible prospective Lead Agencies with the incumbents so that the prospective Lead Agency receives an invitation to present at the Biennial Meeting (there may be more than one meeting).
- FA will:
- Lead Agencies and Interested Parties should be prepared to present at the Biennial Meeting:
- See EFAP Biennial Meeting Presentation Guidelines for Interested Parties (AGR6-2503-010).
- The prospective agency must propose the following:
- Plan for providing services to the Food Pantries.
- Funding breakout (Categories: admin, indirect, operations, food purchases, equipment). See Section 7, Fiscal Management and Reporting.
- Spending plan.
- Types of food that will be purchased and/or delivered.
- Fresh, frozen, shelf-stable, culturally familiar, etc.
- Food procurement policy and sources.
- Sourcing practices – donation, grocery rescue, purchasing, farming/gleaning.
- Food Bank operations.
- Equipment.
- Other.
- Types of food that will be purchased and/or delivered.
- Allocation formula for distributing food and/or funds among the Food Pantries.
- Only Food Pantries participating in the upcoming biennial Agreement period will vote to select the Lead Agency. Lead Agencies are approved by two-third majority vote.
- Be prepared:
- Review the EFAP Procedures Manual.
- Review the required EFAP Biennial Meeting Handout (AGR6-2503-011).
- Review the EFAP Biennial Application (AGR-2205).
- Reach out to participating EFAP Food Pantry Sub Agencies to assess their needs and expectations of a Lead Agency in the communities it intends to serve.
- Interested in becoming a Food Bank?
- Meet the requirements outlined in Section 5.2, Food Bank Sub Agency Eligibility Criteria.
- Immediately contact the current Lead Agency via email or by phone to let them know that your organization is interested in being a Food Bank. You may also contact FA if you are not sure who the current Lead Agency is.
- Timelines will depend upon when the Biennial Meeting is being held (varies county by county).
- Current Lead Agencies hold Biennial Meetings, prior to the start of a new biennium, typically starting in April and running through early June.
- Typically, current Lead Agencies prefer a minimum of 30 days advance notice (exceptions apply due to the Biennial Meeting date).
- At a minimum, provide the current Lead Agency with the following:
- Name and business address of organization, including county.
- Contact person’s name, phone number, and email.
- County(ies) you are interested in providing service to.
- Business description, including mission statement and the organization’s specific work related to hunger-relief.
- Timelines will depend upon when the Biennial Meeting is being held (varies county by county).
- The current Lead Agency will evaluate the eligibility of the prospective Food Bank prior to the Biennial Meeting. This may include:
- An initial meeting.
- A site visit (in-person or virtual).
- The current Lead Agency will notify the prospective Food Bank of its eligibility status in writing (email) prior to the scheduled Biennial Meeting.
- If eligible, the prospective Food Bank will receive an invitation to present at the Biennial Meeting (there may be more than one meeting).
- Be prepared to present at the Biennial Meeting.
- See EFAP Biennial Meeting Presentation Guidelines for Interested Parties (AGR6-2503-010).
- The prospective agency must propose the following:
- Plan for providing services to the Food Pantries.
- Including storage and transportation capabilities.
- Proposed pounds of food and/or services that will be provided.
- Funding breakout (Categories: admin, indirect, operations, food purchases, equipment). See Section 7, Fiscal Management and Reporting.
- Spending plan.
- Types of food that will be purchased and/or delivered.
- Fresh, frozen, shelf-stable, culturally familiar, etc.
- Food procurement policy and sources.
- Sourcing practices – donation, grocery rescue, purchasing, farming/gleaning.
- Food Bank operations.
- Equipment.
- Other.
- Types of food that will be purchased and/or delivered.
- Transportation plan to get the food from the Food Bank to the Food Pantries.
- Plan for providing services to the Food Pantries.
- There can be more than one Food Bank per county.
- The Lead Agency and the Food Pantries will vote to select the Food Bank(s). Food Bank Sub Agencies are approved by two-third majority vote.
- Prospective:
- Review this EFAP Procedures Manual.
- Review the required EFAP Biennial Meeting Handout (AGR6-2503-011).
- Reach out to participating EFAP Food Pantry Sub Agencies to assess their needs and expectations of a Food Bank in the communities it intends to serve. Understanding the network of Food Pantries in the county or multi-county region is crucial to the success of a Food Bank presentation.
- Interested in becoming a Food Pantry?
- Meet the requirements outlined in Section 5.3, Food Pantry Sub Agency Eligibility Criteria.
- Immediately contact the current Lead Agency via email or by phone to let them know that your organization is interested in being a Food Pantry. You may also contact FA if you are not sure who the current county Lead Agency is. Interested Sub Agencies struggling or unable to make contact with the county Lead Agency will receive assistance in the process from FA.
- Timelines will depend upon when the Biennial Meeting is being held (varies county by county).
- Current Lead Agencies hold Biennial Meetings, prior to the start of a new biennium, typically starting in April and running through early June before the deadline to submit applications.
- Typically, current Lead Agencies prefer a minimum of 30 days advance notice (exceptions apply due to the Biennial Meeting date).
- At a minimum, provide the current Lead Agency with the following:
- Name and business address of organization, including county.
- Contact person name, phone number, and email.
- County(ies) you are interested in providing service to.
- Business description, including mission statement and the organization’s specific work related to hunger-relief.
- Timelines will depend upon when the Biennial Meeting is being held (varies county by county).
- The current Lead Agency will evaluate the eligibility of the prospective Food Pantry prior to the Biennial Meeting. This may include:
- An initial meeting.
- A site visit (in-person or virtual).
- The current Lead Agency will notify the prospective Food Pantry of its eligibility status in writing (email) prior to the scheduled Biennial Meeting.
- If eligible, the prospective Food Pantry will receive an invitation to present at the Biennial Meeting (there may be more than one meeting) along with the review of the required EFAP Biennial Meeting Handout (AGR6-2503-011).
- Be prepared to present at the Biennial Meeting.
- See EFAP Biennial Meeting Presentation Guidelines for Interested Parties (AGR6-2503-010).
- Days of operation by week and/or month (frequency) and hours of operation.
- Description of service(s):
- Distribution method (home delivery, drive through, mobile pantry, client choice, other) and location(s).
- Frequency by which a client may receive services (at a minimum monthly). Provide the same level of service and quality of distribution regardless of where an eligible client may reside in the state of Washington.
- Types of food provided – fresh, frozen, shelf stable, culturally familiar, etc.
- Description of the client management system.
- Client data from previous year.
- Service area, including any priority service populations.
- Understanding that regardless of the Food Pantry’s service area, any eligible client in the state of Washington must be served. Food Pantries must provide the same level of service to all clients regardless of where the client resides within the state of Washington.
- Sourcing practices – donation, grocery rescue, purchasing, and farming/gleaning.
- The current Food Pantries and Lead Agency will vote to select any new Food Pantries.
- Duplication of service is the only reason that an otherwise eligible Food Pantry may not be selected.
- If duplication of service is determined, each agency must provide written justification for determination.
- Duplication of service may be determined when two food pantries provide the same services, on the same days, around the same time, in a similar geographical area, targeting a similar population with similar food offerings. This seldom occurs.
- Duplication of service is the only reason that an otherwise eligible Food Pantry may not be selected.
- Be prepared:
- Review the EFAP Procedures Manual.
- Review the required EFAP Biennial Meeting Handout (AGR6-2503-011).
- See EFAP Biennial Meeting Presentation Guidelines for Interested Parties (AGR6-2503-010).
| Click here to return to EFAP page | |
| EFAP Procedures Manual Table of Contents | |
| Section 1 | Section 3 |
| Revision History | |
| Section 2 Revision 2025-09-30 | |
